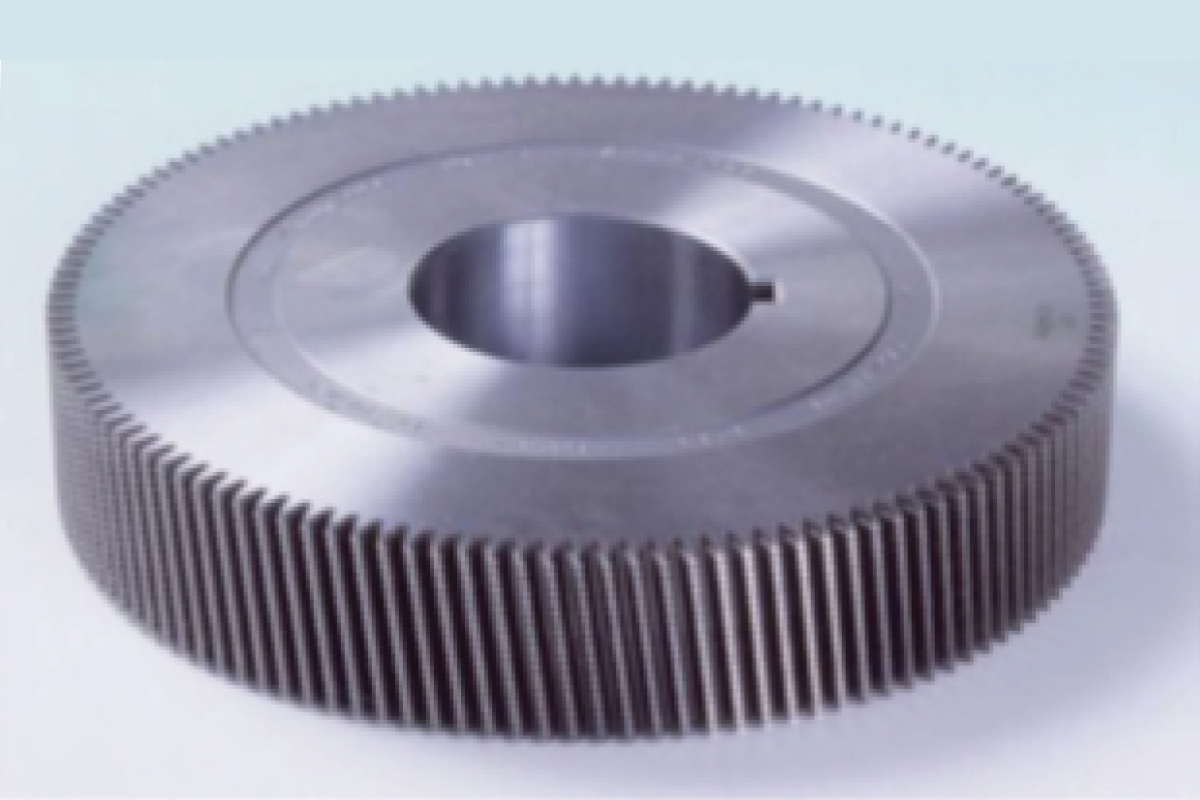

By: Ravi Naik
Input Condition of CNC Blank:
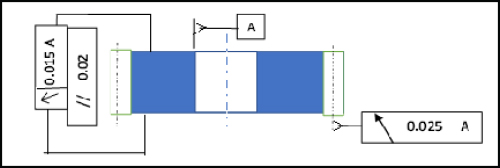
Fig 1: Face runout , Face // & Gear PCD Runout
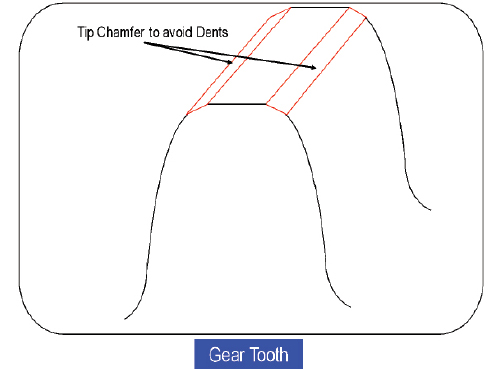
Fig 2: Semi Topping
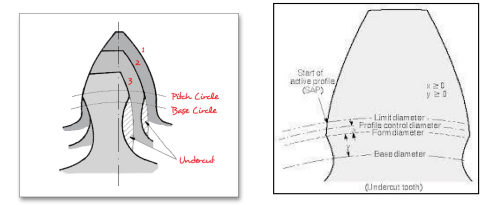
Fig 3: Protuberance pictorial view
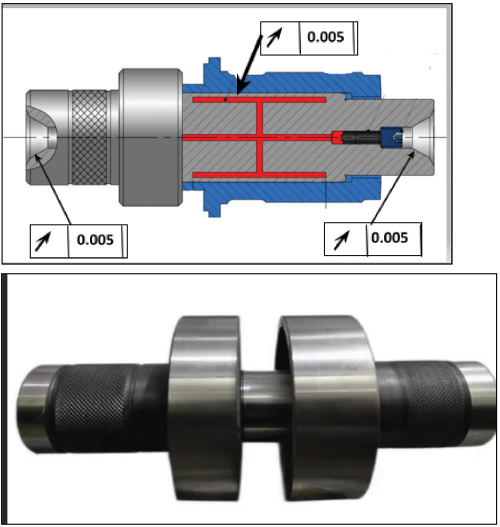
Fig 4: Hydraulic mandrel
Cutter RPM, feed, number passes and dwell time need to be established as per the gear profile angular error and profile crowning required on part.
Types of Shaving:
Part shaving quality effects final part quality; therefore, the shaving process basic conditions must be maintained to achieve required finish gear quality.